5 Proven Mobile App Testing Strategy 2026
- February 13, 2026
- Nabeesha Javed
In 2026, approximately 64% of global traffic comes from mobile devices (Taboola, 2026). As an end-to-end testing services company, we have handled every possible case in mobile app testing. At the C-Suite level, I understand that you have to take the load of mix of technical and organizational challenges.
Strategy 1
Device Fragmentation Mastery
Mobile apps don’t run on just one type of phone. There are different brands, models, OS versions, screen sizes, and hardware power. This variety is called device fragmentation. And it’s one of the biggest reasons apps, crash on specific devices, show broken UI and get rejected by app stores.
Focus on Your Past Data to Cover the Top 80%
Instead of testing on 300+ devices, test only the devices that represent 80% of your users. Most apps can cover 80% of their audience with around 30–35 key devices. Check out your app store analytics and user device reports to analyze the devices. From Data you can reduce unnecessary testing to asave time and reduce unnecessary costs. The other ways are:
Use Cloud Device Farms
Instead of buying and maintaining physical phones, use platforms like BrowserStack. These platforms provide 30,000+ real device configurations, different OS versions, global testing environments, features like GPS simulation, biometrics, network throttling.
Let’s say you’re testing an e-commerce app.
Why This Strategy Works
✔ Focused device coverage
✔ Real-device accuracy
✔ Faster testing cycles
✔ Reduced post-release bugs
✔ Lower infrastructure cost
Proven Strategy 2
Automation-First Pyramid
The Automation-First Pyramid is a smart mobile app testing strategy that focuses on automation at the foundation and keeps slow end-to-end (E2E) tests to a minimum. The idea remains that the more tests you automate at lower levels, the faster and more stable your release cycles become. Many teams report up to 4x faster releases because regression testing becomes quicker and more reliable.
This approach follows the classic testing pyramid model.
- Around 70% of tests are unit or UI automation tests.
- 20% are integration tests.
- 10% are end-to-end tests.
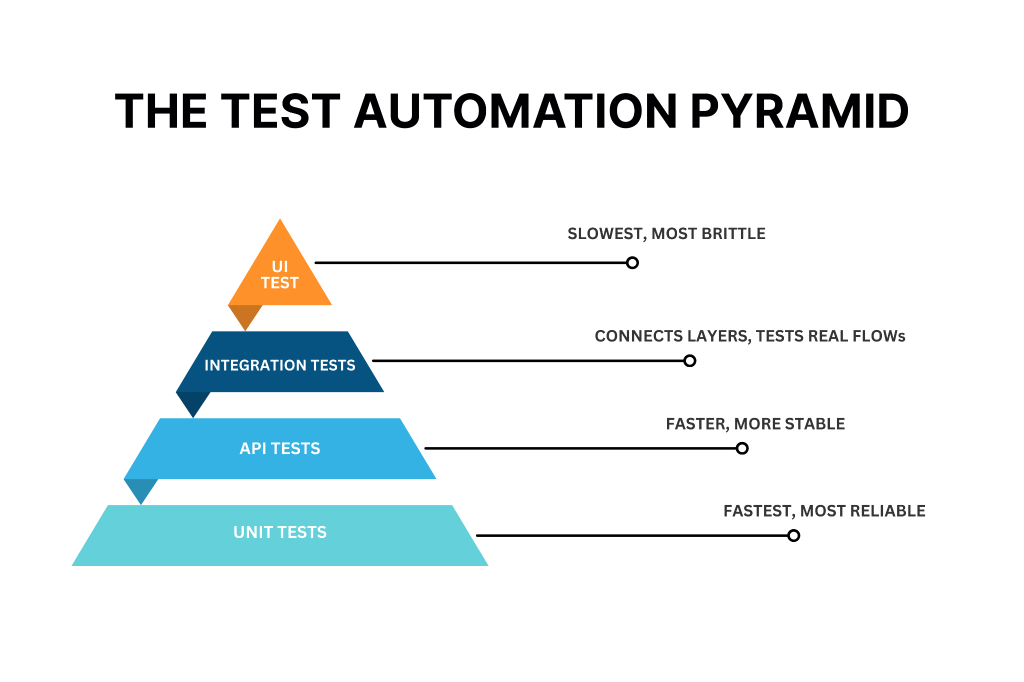
Unit and UI tests validate individual components quickly using tools like Espresso for Android, XCUI Test for iOS and Appium for cross-platform automation. Integration tests verify how modules work together, often using API mocks or database stubs. E2E tests simulate full user journeys, usually executed on cloud device farms.
Automated lower-level tests give quick feedback, while manual testing can focus on exploratory scenarios on real devices. Even Google recommends this balanced 70-20-10 split for Android projects because it ensures stability without slowing development.
Example of Spotify using the Automation First Pyramid
A practical example is Spotify, which adopted this pyramid approach.
They automated most of their unit tests in their Kotlin codebase and maintained a small, efficient E2E suite using Appium.
As a result, regression cycles were reduced from weeks to daily deployments.
Proven Strategy 3:
Performance Under Chaos
Performance Under Chaos is a mobile app testing strategy that prepares apps for extreme real-world conditions. Instead of only testing normal traffic, this approach simulates unpredictable failures such as heavy traffic spikes, slow networks, and server crashes. The goal is to identify weaknesses before users experience them after launch.
This strategy is based on chaos engineering principles, a concept popularized by Netflix. Chaos engineering intentionally introduces failures into a system to test how well it handles disruption. For mobile apps, this means combining load-testing tools like JMeter with device farms to measure memory usage, battery drain, CPU spikes, and UI stability under stress.
One well-known example is Netflix’s Simian Army, which includes Chaos Monkey. This tool randomly shuts down production instances to ensure the system can recover automatically. By applying similar ideas to mobile apps, teams can simulate traffic surges up to 1 million concurrent users, test performance on networks ranging from 5G to unstable edge connections, and monitor key metrics like response times under 2 seconds and crash rates below 5%.
Network variability testing is also important. Tools such as Charles Proxy can throttle network speeds between 100 milliseconds and 2 seconds of latency, simulate packet loss, and test offline behavior. Cloud environments like Amazon Web Services offer fault injection services that help simulate infrastructure-level failures.
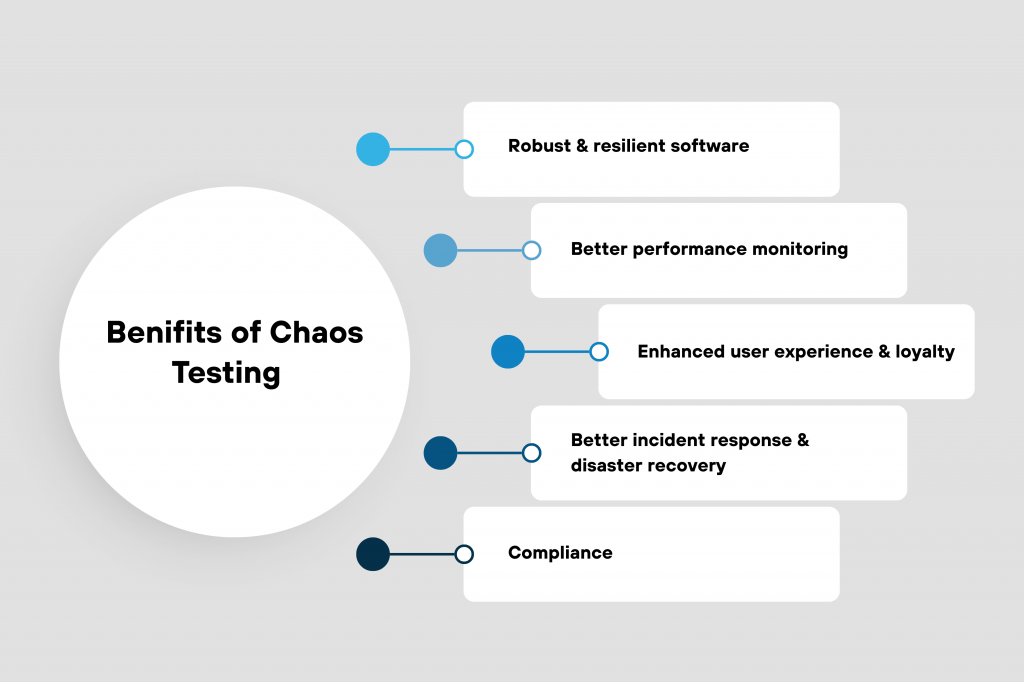
Research-backed findings show that chaos testing can prevent 20–30% of production incidents by exposing system weaknesses early. Netflix itself achieved near zero-downtime scaling during peak loads by continuously testing resilience through controlled failure injection.
For example, a ride-sharing app can use JMeter to simulate one million concurrent ride requests on real devices hosted by BrowserStack, such as a Galaxy S23 running on a 3G network. During testing, engineers might intentionally spike CPU usage to 90% or drop network connectivity by 50%. In one scenario, this process revealed a memory leak that caused a 15% crash rate on iOS 18 devices. After optimization, post-launch incidents dropped by 25%, significantly improving app reliability and user experience.
Proven Strategy 4: Security-by-Design Integration
Security-by-Design Integration is a mobile app testing strategy that builds security directly into the development and testing pipeline instead of treating it as a final step. The idea is to “shift security left,” meaning vulnerabilities are identified early during development through automated scans and continuous monitoring in CI/CD workflows.
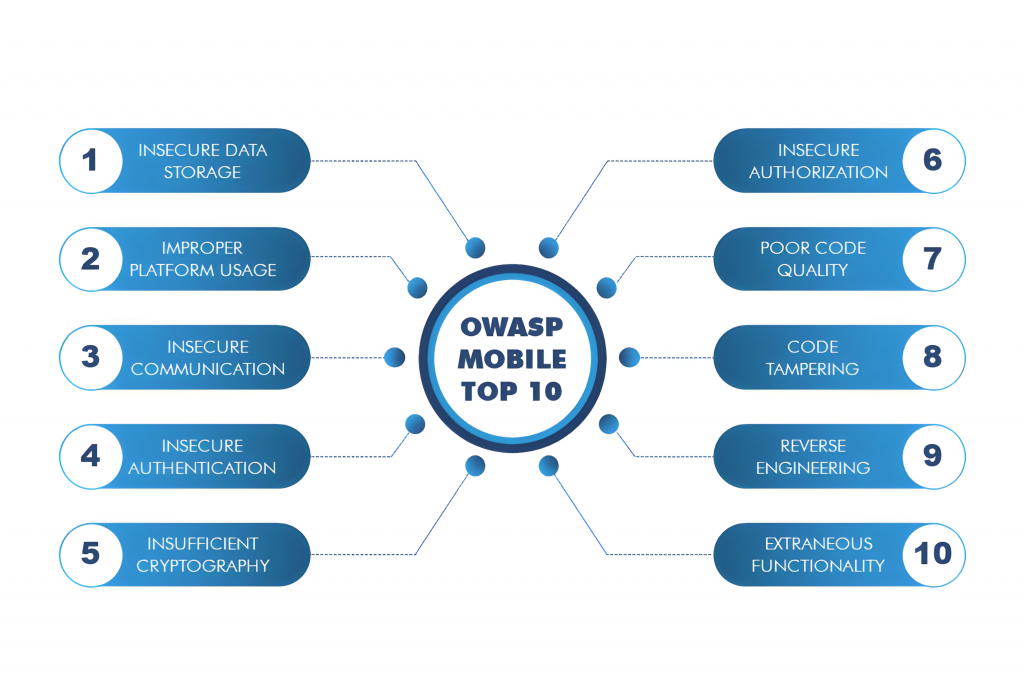
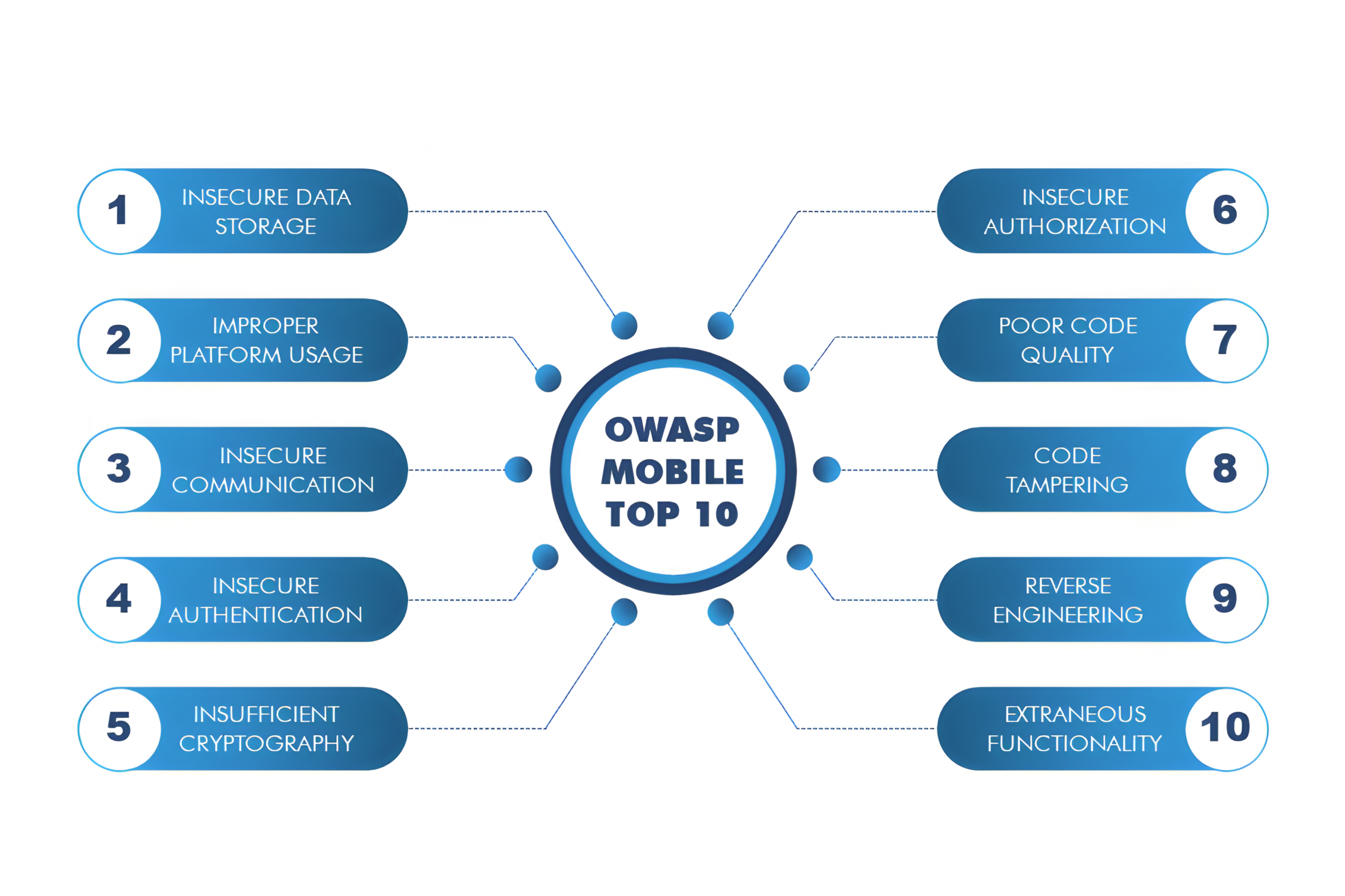
This strategy focuses on the OWASP Mobile Top 10 risks, which include issues like improper credential usage, insecure communication, insecure data storage, and weak cryptography. Instead of manually checking for these problems, teams automate security testing using tools such as OWASP ZAP for dynamic analysis and MobSF for static analysis. These tools scan the application during runtime and in source code to detect exploitable weaknesses.
Security checks can also be integrated with UI automation frameworks such as Detox and Appium, allowing automated security validation during login flows, payment processes, and other sensitive user journeys. In addition to scanning, runtime protections strengthen the app after deployment. Techniques such as code obfuscation with ProGuard, advanced protection with DexGuard, certificate pinning, root detection, and Runtime App Self-Protection (RASP) help defend against tampering and reverse engineering.
The benefits of this approach are significant. Industry reports show that embedding security gates in DevSecOps pipelines can reduce breach incidents by up to 60%. For example, Chase Bank has strengthened its mobile security posture through proactive vulnerability scanning and automated security controls. Identifying issues before production dramatically lowers remediation costs and helps avoid compliance penalties or data leaks.
A practical example would be a banking app integrating OWASP ZAP into its Appium-based CI pipeline. During automated login testing on platforms like BrowserStack, ZAP scans for insecure authentication issues such as weak session tokens. Detox end-to-end tests can check for privacy leaks or exposed data. Additional runtime checks detect rooted or jailbroken devices. In one scenario, automated scanning identified a hardcoded API key vulnerability before release, preventing potential data exposure and strengthening overall app resilience.
Proven Strategy 5: User-Centric Exploratory Testing
User-Centric Exploratory Testing blends automation with real human testing to uncover issues that scripts often miss. While automation ensures core functionality works correctly, exploratory testing focuses on how real users actually experience the app. Platforms like Kualitatem, Testlio and uTest provide access to global testers who use the app in unscripted sessions across different regions, devices, and cultural contexts.
The core idea is simple: humans notice things automation cannot. Exploratory testers simulate real-world behavior such as unusual gestures, multitasking interruptions, poor network conditions, accessibility challenges, or region-specific language layouts. For example, testers from 100+ locales can identify cultural UX mismatches, translation errors, layout breaks, or confusing flows that automated scripts would not detect.
This strategy also links testing results to measurable user satisfaction metrics. After each exploratory session, teams collect Net Promoter Score (NPS) feedback to track how UX improvements affect user perception. By comparing pre-test and post-test scores, companies can measure UX maturity and aim for meaningful improvements, such as a 20-point increase per iteration.
Research from Google during Material Design testing showed that exploratory methods uncovered significantly more usability defects compared to automation alone. Organizations using this hybrid approach report higher first-pass app store approval rates and lower post-launch rework costs, leading to faster releases and substantial long-term savings.
As a C-suite executive leading a premier quality assurance firm specializing in mobile app testing, our strategy prioritizes scalable excellence to safeguard client brands and drive revenue growth. We deliver authoritative, data-backed approaches proven across the UAE.