How to Align Cybersecurity Risk Assessments with Business Objectives

- January 2, 2026
- Zunnoor Zafar
Cybersecurity is no longer just an IT concern. It has now become a core business priority in modern days. Organizations transform digitally with time. They try to increase their presence online for better growth.
But this comes with a price. It’s when organizations have a high online presence, they’re more prone to cyber attacks. Such an attack can directly impact business continuity. It hinders growth and affects reputation. So, to avoid this, it’s important to align cybersecurity risk assessments with business objectives.
Doing so ensures that the security strategies not only protect assets. But they also drive value and support organizational goals. How are organizations supposed to do that? Well, let’s discuss.
Key Takeaways
- Cybersecurity risk assessments work best when they are directly connected to business goals like growth, customer trust, and compliance.
- Focusing security efforts on the most critical business assets helps organizations use time and resources more wisely.
- Bringing cybersecurity and QA teams into planning early prevents major risks during launches and digital transformation.
- Clear business-friendly metrics allow leaders to understand security risks and make better decisions.
- Regular testing, monitoring and updates are necessary to keep security aligned with changing business needs and threats.
Why does the Alignment Matter So Much?
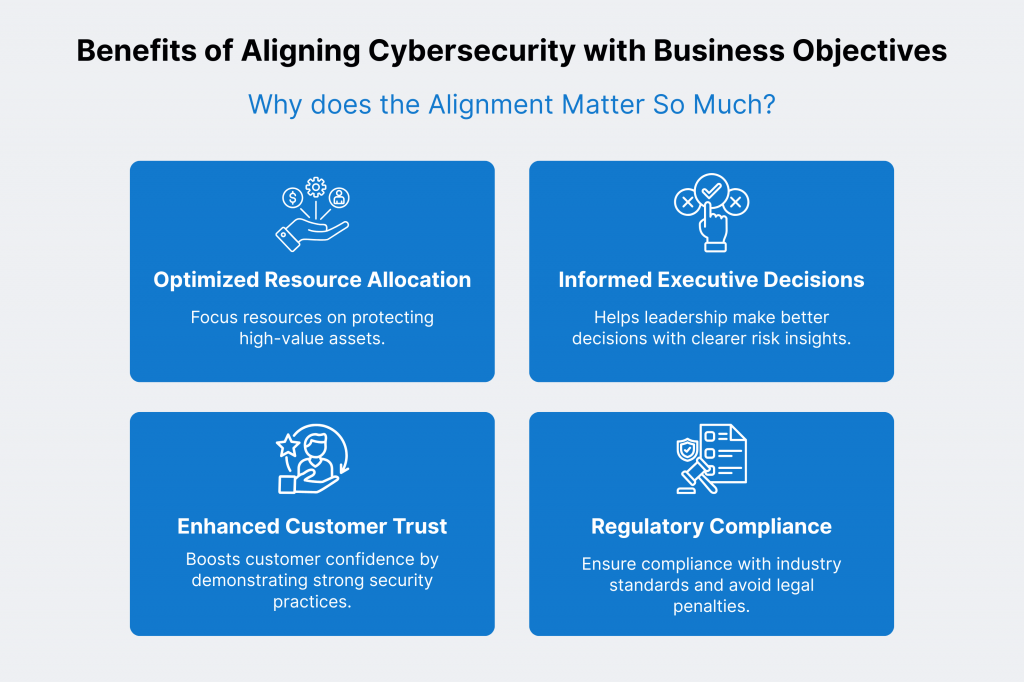
Cybersecurity risk assessments help organizations identify threats to their assets. But the thing is that you’re not supposed to conduct these assessments in isolation from business objectives. Because then, they may fail to address the most significant risks.
And not just that, opportunities to support business growth might also be missed. So, by aligning cybersecurity with business strategy, organizations get the following benefits.
- More resources can be spent on protecting what matters most.
- Informed decisions can be made at the executive level.
- Trust with customers and partners can be improved.
- Regulatory requirements can be fulfilled.
Steps to Align Cybersecurity Risk Assessments with Business Objectives
The following are some of the main steps that organizations have to take in order to do this.
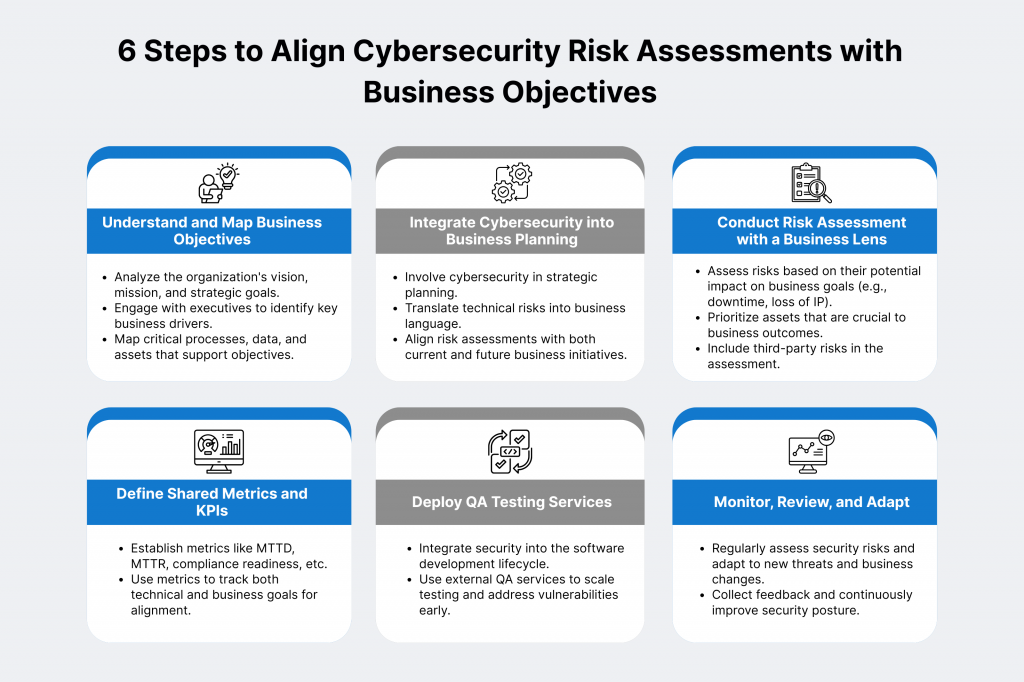
Step 1: Understand and Map Business Objectives
This is the very foundation for the alignment. There has to be a deep understanding of what the organization’s mission is. The vision, the strategic goals have to be analyzed.
Cybersecurity teams should engage with the executives of the organization. Ask them what the key business drivers are. They can be things like revenue growth, market expansion, or even innovative ideas for the future.
Once that’s done. They are recommended to map critical processes along with the data and assets to support these objectives. Lastly, cybersecurity teams are required to recognize the regulatory and compliance requirements. Ones that are relevant to the industry.
Also, here’s a tip for organization executives: To make things easier for everyone, conduct workshops and cross-functional meetings. Doing so will ensure that the teams are aware of business priorities.
Step 2: Integrate Cybersecurity into Business Planning
Cybersecurity should never be treated as an afterthought. Or just as one step in digital operations. Instead, organizations must embed it in business planning. This includes doing the following things.
- Including cybersecurity team leads in strategic planning sessions.
- Conveying technical risks into easy language so everyone can understand them. For example, how a data breach could impact revenue.
- Ensuring that risk assessments consider both the current and future business initiatives. Think digital transformation or new product launches.
For your better understanding, here’s an example:
Let’s say your organization is launching a new customer-facing application. You must involve cybersecurity and QA testing services early to identify potential vulnerabilities and compliance risks.
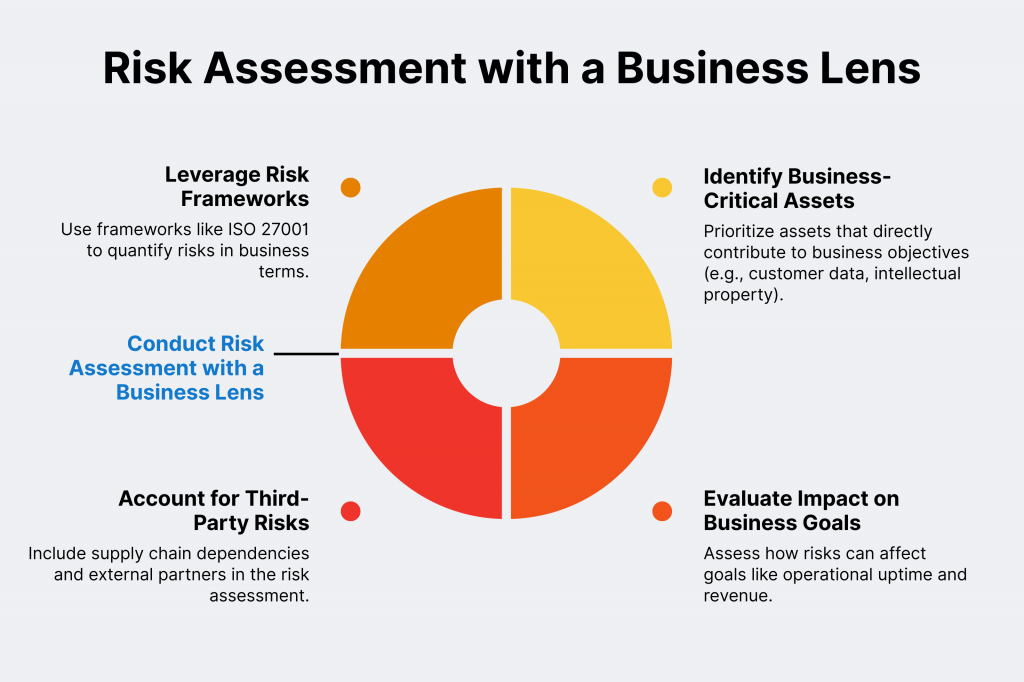
Step 3: Conduct Risk Assessment with a Business Lens
Traditional risk assessments focus only on one thing. Technical vulnerabilities. However, aligning them with business objectives requires a broader approach.
To do it, first assess risks based on their potential impact on business goals. i.e., operational downtime and loss of intellectual property. Then, prioritize assets and processes that are most important to achieving required business outcomes. Once that’s done, it’s time to consider third-party risks. They can be supply chain dependencies and regulatory obligations.
Most experts recommend making use of frameworks like ISO 27001 or FAIR. They help quantify risk in business terms. And enable clearer communication within organizations and with stakeholders.
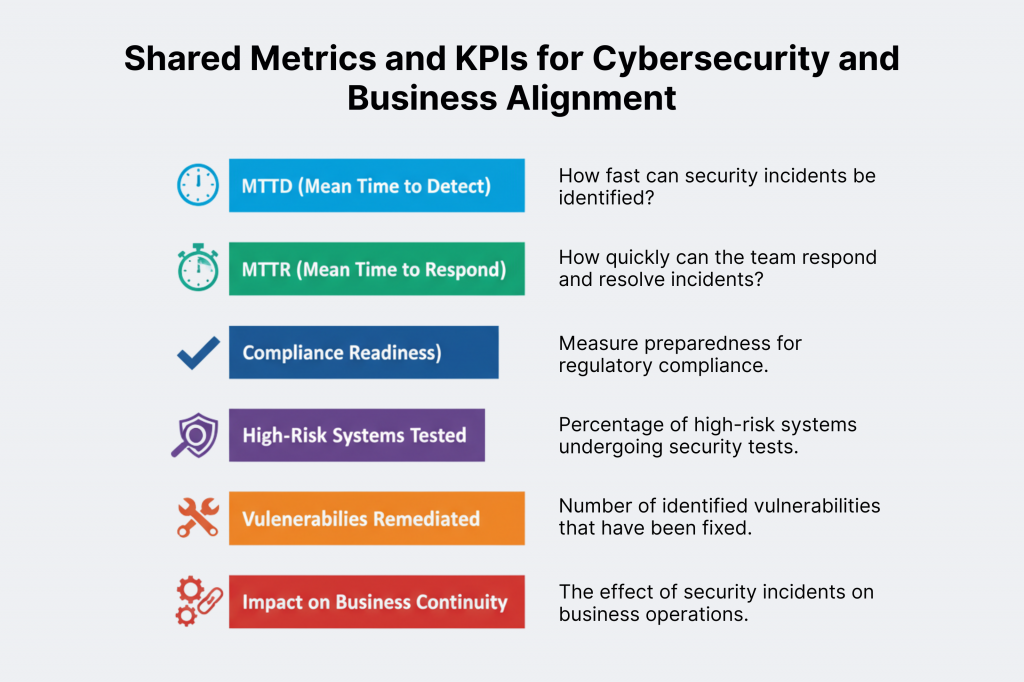
Step 4: Define Shared Metrics and KPIs
Alignment. Everybody being on the same page. This is something that has to be achieved by an organization in order to grow and succeed.
To get to this goal, metrics have to be established. Ones that resonate both with technical and business audiences. Usually, they include:
- Mean time to detect (MTTD) and Mean time to respond (MTTR) to incidents.
- Compliance readiness scores.
- Percentage of high-risk systems tested.
- Number of vulnerabilities remediated.
- Impact on business continuity and customer satisfaction.
Besides these, QA metrics, like defect density and test coverage, can also be adapted. They’ll enable measuring the effectiveness of security controls and processes.
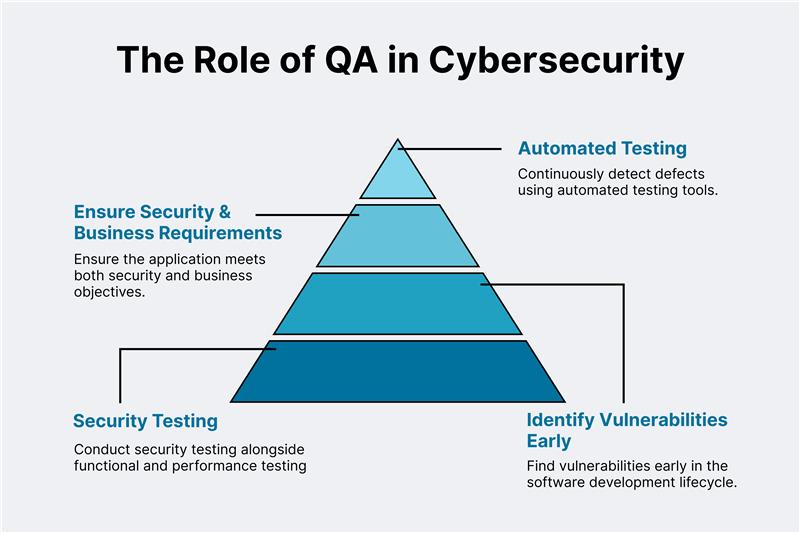
Step 5: Deploy QA Testing Services
QA testing services play an important role in integrating security into the software development lifecycle. Besides the testers available inside an organization, it’s always a good idea to get external help. This way, an organization can increase or decrease the workforce as needed. That said, QA services include roles. Which are:
- Conducting security testing alongside functional and performance testing.
- Identifying vulnerabilities early and the development lifecycle.
- Ensuring that software applications meet both security and business requirements.
- Implementing automated testing to detect defects continuously.
When quality assurance is done while keeping the security of an application in mind, organizations can tackle issues before they impact business operations.
Additionally, to put their resources to good use, organizations are recommended to deploy QA testing services only from top-notch providers. Like Kualitatem.
Step 6: Monitor, Review, and Adapt
Threats and business environments are constantly changing. Organizations have to maintain alignment in the long run. To do that, regular risk assessments and audits are needed.
Furthermore, risk models and controls also have to be updated based on new threats and business changes.
One thing we recommend here is to put the feedback provided by the QA team to good use. Listen to their suggestions and ask the developers to implement them if they look useful.
Lastly, monitor and make reports on security incidents. Keep a tab on the lessons learned and improvements made. Doing so will enable organizations to ensure that a particular security issue doesn’t happen again.
Kualitatem’s Case Study: Aligning Cybersecurity in a Digital Transformation Project
To put into perspective how cybersecurity risk assessments are aligned with business objectives, we’d like to present a case study.
A leading financial organization from KSA embarked on a digital transformation initiative. It wanted to launch a new mobile banking app. The organization’s business objectives included enhancing customer experience. As well as increasing market share and ensuring regulatory compliance.
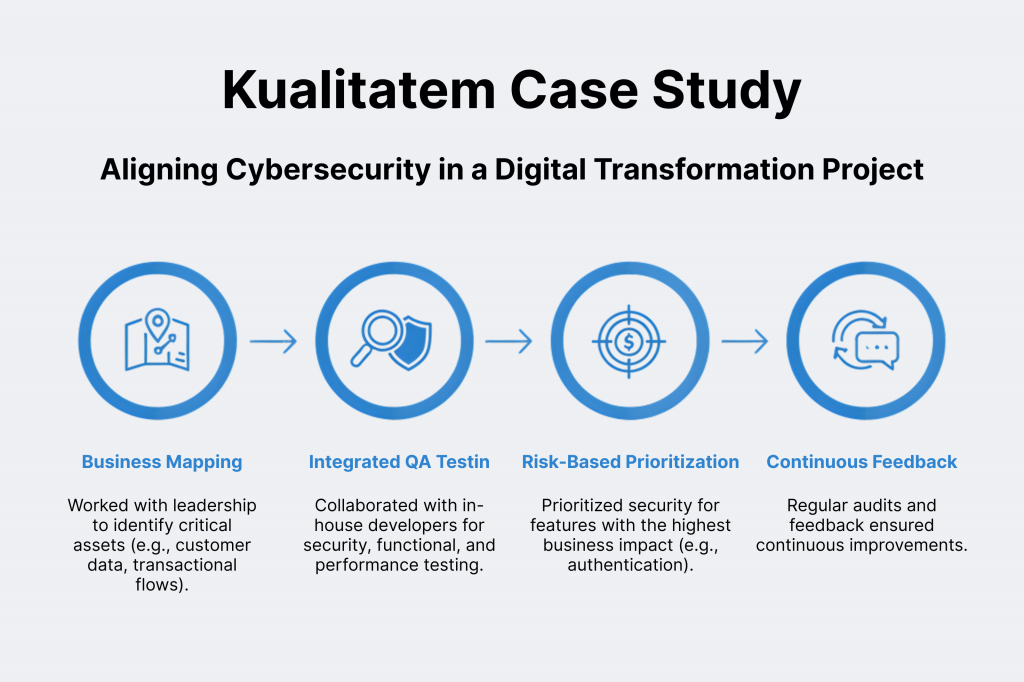
Here’s how the alignment was achieved by Kualitatem:
- Business Mapping: Our cybersecurity team worked with the organization’s leaders to identify important assets and regulatory requirements. In this case, the assets were customer data and transactional flows.
- Integrated QA Testing: The QA team collaborated with the organization’s in-house developers. They did it to conduct security, functional, and performance testing throughout the development lifecycle.
- Risk-Based Prioritization: Security controls were prioritized for features with the highest business impact. These included authentication and transaction processing.
- Continuous Feedback: Once everything was done, we conducted regular audits and asked the organization to get user feedback. These things enabled continuous improvements, ensuring the app remained secure and aligned with business goals. Even in the long run.
So, what was the outcome of doing all this? Well, the app launched successfully. There were no major security incidents. The customer satisfaction was high, along with full regulatory compliance.
If you want something similar done, contact Kualitatem today.
Conclusion
For organizations looking to thrive, it’s important to align cybersecurity risk assessments with business objectives. There are 6 steps to do so.
First, there has to be an understanding of the business objectives. Then comes the integration of cybersecurity in business planning. The third step is to conduct a risk assessment with a business lens, while the fourth includes defining shared metrics.
Fifth step is to deploy QA testing services from external sources. And lastly, organizations have to monitor, review, and adapt to the changing threats and business goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1) What is the difference between a cybersecurity risk assessment and a security audit?
A risk assessment looks at possible future threats and their business impact. A security audit checks if current controls follow required standards and policies.
Q2) How often should cybersecurity risk assessments be updated?
They should be reviewed after major business or technology changes. Even without changes, an annual update helps keep risks under control.
Q3) Is cybersecurity risk alignment useful for small businesses?
Yes. It helps smaller teams focus limited budgets on protecting their most important systems and data.
Q4) Why are third-party vendors a cybersecurity risk?
Vendors often access systems or data. Weak vendor security can expose organizations to breaches they do not directly control.